Collection: IgG/IgM Antibodies
IgG/IgM antibodies are two classes of antibodies produced by the immune system in response to infections. These antibodies are commonly tested to determine if a person has been exposed to a particular pathogen, such as a virus or bacteria.
- IgM (Immunoglobulin M): This is the first antibody produced by the immune system when a new infection occurs. Its presence indicates a recent or acute infection.
- IgG (Immunoglobulin G): This is produced later during the course of an infection and can persist for a longer time, sometimes for years, indicating past exposure or long-term immunity.
Testing for IgG/IgM antibodies is often done in the context of infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, dengue, or other viral/bacterial infections, to assess whether a person is currently infected (IgM) or has developed immunity (IgG).
Point-of-Care (POC) Benefits
Point-of-care (POC) testing refers to medical testing that is performed near or at the site of patient care, typically providing rapid results. POC tests for IgG/IgM antibodies (often in the form of rapid diagnostic tests) offer several benefits:
Rapid Results: Most POC IgG/IgM antibody tests provide results within 10-30 minutes, allowing immediate decision-making for treatment or isolation if needed.
Convenience: POC tests can be performed at clinics, hospitals, or even at home, eliminating the need to send samples to a central laboratory.
Early Detection: Detecting IgM antibodies can help identify acute infections early, allowing for quicker interventions and reducing the risk of transmission.
Monitoring Immunity: IgG testing helps assess whether someone has developed immunity from a past infection or vaccination, which is particularly useful for managing diseases like COVID-19.
Cost-effective: POC tests are generally cheaper than laboratory-based tests, reducing healthcare costs and improving accessibility.
-
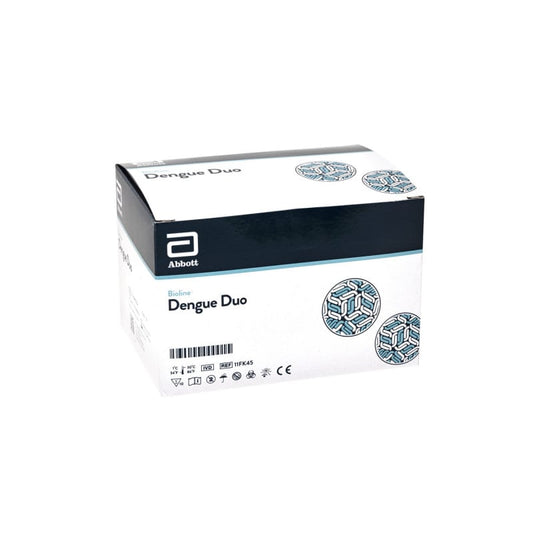
Bioline™ Dengue Duo 25 Tests
Regular price £356.51 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £356.51 GBP -
Bioline™ HCV Antibody Rapid 30 Tests
Regular price £410.85 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £410.85 GBP -
Bioline™ HCV Antibody Rapid 25 Tests
Regular price £381.66 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £381.66 GBP -
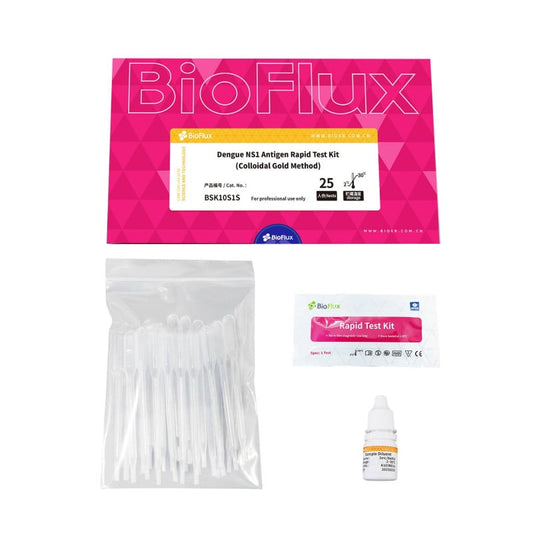
BIOFLUX Dengue NS1 Antigen Rapid 25 Tests
Regular price £154.24 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £154.24 GBP -
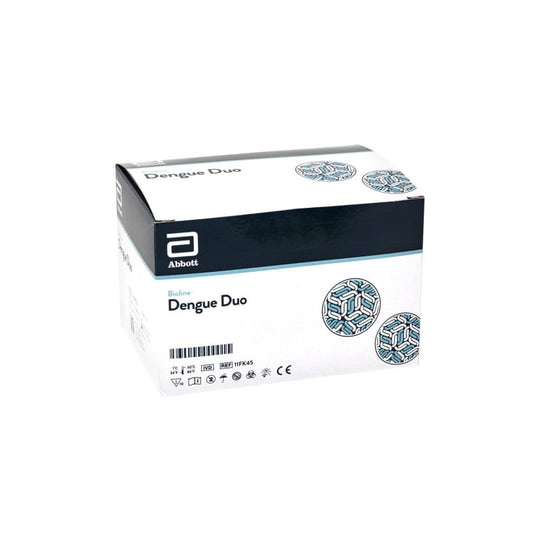
Bioline™ Dengue Duo 10 Tests
Regular price £183.43 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £183.43 GBP -
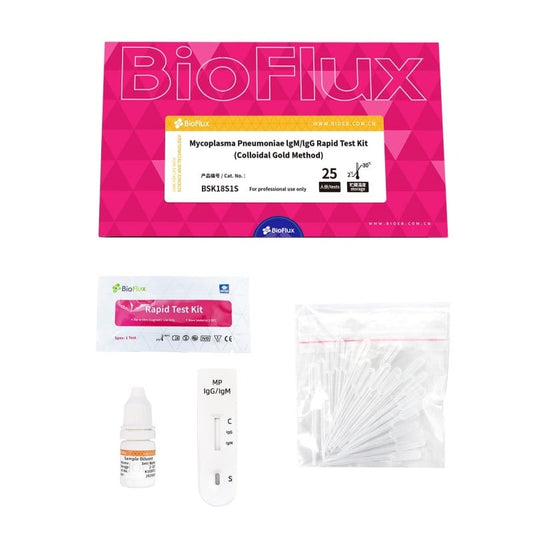
BIOFLUX Mycoplasma Pneumoniae IgM/IgG Rapid 25 Tests
Regular price £137.45 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £137.45 GBP -
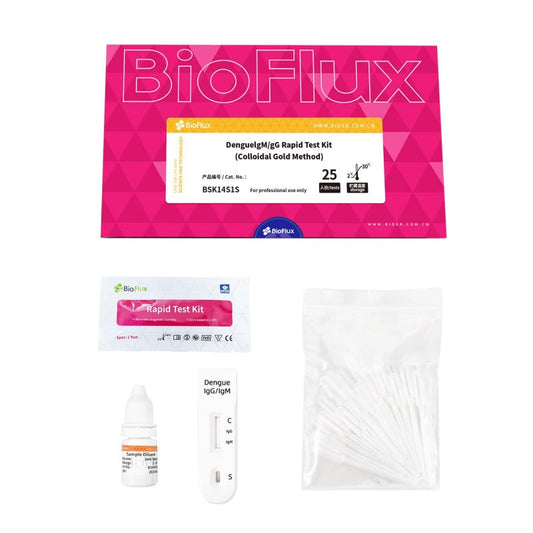
BIOFLUX Dengue IgM/IgG Rapid 25 Tests
Regular price £137.45 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £137.45 GBP -
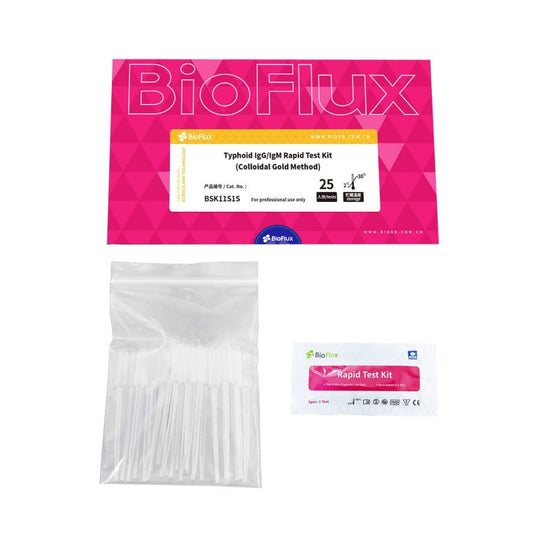
BIOFLUX Typhoid IgG/IgM Antibody Rapid 25 Tests
Regular price £133.80 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £133.80 GBP -
Bioline™ Syphilis 3.0 Rapid 30 Tests
Regular price £90.71 GBPRegular priceUnit price / per£0.00 GBPSale price £90.71 GBP